Difference Between OKR (Objective and Key Result) and MBO (Management by Objectives)


“If you desire to make a difference in the world, you must be different from the world.”— Elaine S. Dalton
Introduction
There are different ways to reach locations A to B. The important perspective is to identify a path wherein we can reach the destination at the lowest cost, with high efficiency and within the timeframe. Once we reach our desired location, the next time, rather than following the same path, we can explore better possibilities so that we can improve further.
Read More: https://bit.ly/ObeyaRoom
Objective
Managing talent and organizational objectives is critical for success. It ensures employees can identify and work towards common goals, encourages responsibility, ownership and autonomy within a role, and assists in executing overall organizational strategy.
There are multiple ways to manage this. Two goal-setting frameworks are MBO and OKR and whilst both are inherently designed to track, manage, and appraise output, there are few distinct differences between both approaches.
Once you read this blog, you will understand, what is MBO, what is OKR, the differences between MBO and OKR, the benefits of OKRs versus MBOs and why OKRs are better than MBOs for effective goal setting.
Read More: https://bit.ly/DOJOCentre
Definition:
Efficiency (Cl 3.7.10): Relationship between the results achieved and the resources used.
Effectiveness (Cl 3.7.11): The extent to which planned activities are realized and planned results are achieved.
Read More: https://bit.ly/5SSteps
Detailed Information
What is MBO?
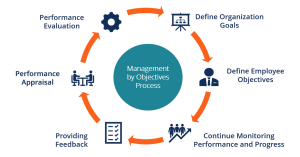 Author Peter Drucker was the first person to use the term ‘management by objective’. That was way back in 1954 in a book called The Practice of Management. MBO is an acronym for Management by Objectives. It can be defined as a management system that measures employees’ performance against a series of set targets or goals to gauge their overall performance in their role. These objectives are often tied into those set for the overall business or department.
Author Peter Drucker was the first person to use the term ‘management by objective’. That was way back in 1954 in a book called The Practice of Management. MBO is an acronym for Management by Objectives. It can be defined as a management system that measures employees’ performance against a series of set targets or goals to gauge their overall performance in their role. These objectives are often tied into those set for the overall business or department.
Management by objectives (MBO) uses a set of quantifiable or objective standards against which to measure the performance of a company and its employees. By comparing actual productivity to a given set of standards, managers can identify problem areas and improve efficiency. Both management and workers know and agree to these standards and their objectives.
Examples of MBOs include:
- Decrease operational costs by 5%
- Add one new customer
- Increase win ratio by 8%.
Read More: https://bit.ly/HoshinKanriPolicy
What is OKR (Objectives and Key Results)
 “OKR” stands for Objectives and Key Results. OKRs are an effective goal-setting and leadership tool for communicating what the organization wants to accomplish and what milestones they will need to meet to accomplish it. OKRs are used by some of the world’s leading organizations to set and enact their strategies like Google. OKRs are typically written with an Objective at the top and 3-5 supporting Key Results below it.
“OKR” stands for Objectives and Key Results. OKRs are an effective goal-setting and leadership tool for communicating what the organization wants to accomplish and what milestones they will need to meet to accomplish it. OKRs are used by some of the world’s leading organizations to set and enact their strategies like Google. OKRs are typically written with an Objective at the top and 3-5 supporting Key Results below it.
An Objective is simply what is to be achieved. By definition, Objectives are significant, concrete, action-oriented, and (ideally) inspirational.
Key Results benchmark and monitor how we get to the Objective. Effective KRs are specific, time-bound, and aggressive yet realistic. Most of all, they are measurable and verifiable.
The OKR methodology was created by Andy Grove at Intel and taught to John Doerr (Book: Measure What Matters) by him. Since then, many companies have adopted them, including Google and Netflix.
Read More: https://bit.ly/MBObjective
Example of OKR:
Objective: Increase sales by 20%
Key Results:
- Add 5 new promotional items
- Increased social media presence and advertisement by 10%
- Grow marketing leads by 10%
Read More: https://bit.ly/DailyWorkManagement
Difference Between MBO and OKR
 Management by Objectives (MBO) and Objective and Key Results (OKR) are two popular goal-setting systems for high-performance teams. They are also similar because OKRs evolved from MBOs. Like MBOs, OKRs are a framework for setting strategic goals. Both MBOs and OKRs involve writing an internal statement of outcomes that an organization wants to achieve. MBO goal setting focuses on the “what,” while OKRs go one step further than MBOs by including a set of measures of progress.
Management by Objectives (MBO) and Objective and Key Results (OKR) are two popular goal-setting systems for high-performance teams. They are also similar because OKRs evolved from MBOs. Like MBOs, OKRs are a framework for setting strategic goals. Both MBOs and OKRs involve writing an internal statement of outcomes that an organization wants to achieve. MBO goal setting focuses on the “what,” while OKRs go one step further than MBOs by including a set of measures of progress.
| S.No. | MBO (Management by Objectives) | OKR (Objectives and Key Results) |
| 1 | Focus on ‘What’: Objectives | Focus on ‘What’ and ‘How’: Objectives and related Key Result Areas |
| 2 | Annual Review | Monthly or Quarterly Review |
| 3 | Information access is ‘Private (siloed)’ | Information access is ‘public and transparent |
| 4 | The approach is ‘Top-Down’ | The approach is ‘Bottoms-up and sideways’ also |
| 5 | The performance is linked with ‘Compensation’ | The performance is not linked with ‘Compensation’ |
| 6 | Limited or no ‘Risk’ | ‘Aggressive and Aspirational’ in approach |
| 7 | Assigned to ‘Individual’ | Assigned to a ‘Team and their performance’ |
Read More: https://bit.ly/BalancedScorecard1992
References:
ISO 9001: 2015
ISO 9002: 2016
ISO 9004: 2018
IATF 16949: 2016
Industry Experts
This is the 181st article of this Quality Management series. Every weekend, you will find useful information that will make your Management System journey Productive. Please share it with your colleagues too.
In the words of Albert Einstein, “The important thing is never to stop questioning.” I invite you to ask anything about the above subject. Questions and answers are the lifeblood of learning, and we are all learning. I will answer all questions to the best of my ability and promise to keep personal information confidential.
Your genuine feedback and response are extremely valuable. Please suggest topics for the coming weeks.

Recent Comments