FMEA: AIAG/VDA Handbook: 7 Steps (1st Edition: 2019)


The only people who see the whole picture are the ones who step out of the frame: Salman Rushdie
Introduction
There are 7 steps to success.
- Set your goals
- Commit yourself
- Make adjustments
- Be consistent
- Expect to succeed
- Take pride
- Have enough
Objective
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a well-established method in the manufacturing industry, commonly applied to optimize product/process reliability and cost. It requires cross-functional teams to identify and evaluate the product/process functions, to continuously improve them to reduce risks. The FMEA is a living document and is re-evaluated many times during its lifecycle.
The purpose of the 7 steps as per FMEA Handbook: AIAG & VDA 1st Edition 2019 is aimed at facilitating complete understanding about establishing the content of the documentation, documenting the effectiveness of the actions taken and assessment of the risk after the action is taken, communicating the actions to reduce risk within the organization, customer, supplier and finally recording the risk analysis & risk reduction.
Detailed Information
FMEA (Failure Mode & Effect Analysis) is a team-oriented, systematic, qualitative and analytical method to identify, analyse and mitigate the technical risks related to the ‘product and manufacturing process design.
The FMEA is the ‘Before the Event’ and not the ‘After the Event’ exercise.
The effectiveness of the FMEA can be gauged from the improvement in COQ (Cost of Quality) and COPQ (Cost of Poor Quality)
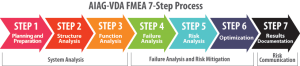
7 Step Process:
- Planning & Preparation: Objectives, Project identification, plan boundaries
- Structure Analysis: Process Item, Process step, process work element
- Function Analysis: Intended Function/Requirement
- Failure Analysis: Failure Effect, Failure Mode, Failure Cause
- Risk Analysis: Prevention and Detection Control, Severity / Occurrence / Detection
- Optimization: Recommended Actions, Responsibility, target date, revised S, O, D
- Result Documentation
Step 1 (Planning and Preparation)
5 key objectives:
- Project identification and boundaries
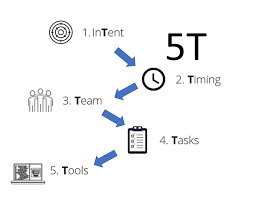
- Project plan (5T): InTent, Timing, Team, Task, Tools
- Analysis boundaries: what needs to be included and excluded
- Identification of baseline FMEA with the lesson learned
- The basis for step 2 (Structure Analysis)
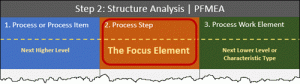
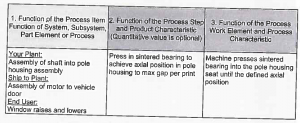
Step 2 (Structure Analysis)
6 key steps:
- Facilitating a complete understanding of the Product/Process.
- Identify and break down the Product/Process into sequential steps, interfaces and logistical elements by using a Process Flow Chart, Structure Tree and Boundary diagram
- Collaboration between customer and organization
- Identify each stage, interface and logistical element in the process at hand.
- Input for the Functional Analysis (Step 3)
- Consists of three expanded columns whose purpose is to facilitate a thorough understanding of the process. Start with the Focus Element in the “middle column,” then identify the Process of which the Focus Element is a part and finally identify all Process Work Elements of the Focus Element.
Step 3 (Function Analysis)
6 Key Objectives:
- Exploration of what the product should be doing in the Function Analysis step from a technical point of view
- Creation of a functional tree/network and a functional analysis form and P-diagram (DFMEA) or process flow chart (PFMEA)
- Using the Structure Analysis (step 2), detailed gradation of the external and internal customer functions and their requirements in the analysis
- Linking of the defined requirements and The focus is on the question: ‘what does the thing that we want to analyze DO?
- Precise definition as the basis for the 4th step (the failure analysis)
- Detailed graphical representation of the function (visualization)
Step 4 (Failure Analysis)
4 Key objectives:
- Establishment of the failure chain
- Identification of potential Failure Effects, Failure Mode and Failure Causes for each product/process function
- Understanding the Failure Effect to the Customer and the supplier
- Performed for each element/step in the process description (Structure Analysis-Step 2 and Function Analysis-Step 3)
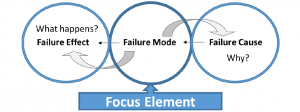
Failure Chain:
- Failure Modes (FM): It means the ways, or modes, in which something might fail.
- Failure Effect (FE): It refers to studying the consequences of those failures’ mode.
- Failure Cause (FC): A indication of why failure mode could occur
Step 5 (Risk Analysis)
7 Key Objectives:
- Assignment of existing or planned controls and rating of failure
- Assignment of preventive control to the failure causes
- Assignment of detective control to the failure causes or failure modes
- Rating for Severity, Occurrence and Detection for each failure chain
- Evaluation of action priority
- Collaboration between customer and supplier related to the severity
- The basis for the optimization step (Step 6)
Severity (S): Severity of the Failure Effect (FE)
Occurrence (O): Occurrence of the Failure Cause (FC)
Detection (D): Detection of the Failure Cause (FE) and/or Mode (FM)
Severity Table: Rated from Very High (10) to Very Low (1)
Occurrence: Rated from Extremely High (10) to Extremely Low (1)
Detection: Rated from Very Low (10) to Very High (1)
Action Priority (AP)
The key objective of ‘Action Priority’ is to choose, how to best prioritize the efforts to reduce the risk.
Priority High (H):
- Highest priority for review and action.
- Either identify an appropriate action to improve prevention and/or detection
- Or justify and document why current controls are adequate
Priority Medium (M):
- Medium priority for review and action.
- Either identify an appropriate action to improve prevention and/or detection
- Or at the discretion of the organization, justify and document why controls are adequate
Priority Low (L):
- Low priority for review and action.
- Could identify actions to improve prevention or detection controls
Step 6 (Optimization)
9 Key Objective:
- Identification of actions necessary to reduce the risk and increasing customer satisfaction by improving the product and process design
- Assignment of the responsibility and target date for action implementation
- Implementation and documentation of the action taken
- Verifying the effectiveness of the implemented actions
- Assessment of the risk after the action is taken (S, O, D)
- Collaboration between CFT and other relevant interested parties like the customer, supplier, process owner etc.
- The actions should be implementable and not potential actions which may never be implemented
- Capture ‘Things Gone Wrong (TGR)’ for future FMEA analysis
- Commitment to review and revise FMEA during mass production, Design change, corrective actions
Step 7 (Results Documentation)
5 key objectives:
- Communication of the results and conclusion of the analysis
- Establish: Content of the documentation
- Documentation: Effectiveness of the actions taken and assessment of the risk after action taken
- Communication: Actions to reduce risk within organization, customer, supplier
- Record: Risk analysis, risk reduction
Present Challenges
- How often the cross-functional team is clear about the requirements of steps 1 to 7?
- How often the FMEA is a LIVE document and is reviewed & updated in case of any design change, corrective action, Things Gone Wrong?
- How often the top management is monitoring the effectiveness of the FMEA by comparing COQ and COPQ before and after the implementation of FMEA?
References:
IATF 16949: 2016
FMEA Handbook (AIAG-VDA 1st Edition June 2019)
Industry Experts
This is the 129th article of this Quality Management series. Every weekend, you will find useful information that will make your Management System journey Productive. Please share it with your colleagues too.
In the words of Albert Einstein, “The important thing is never to stop questioning.” I invite you to ask anything about the above subject. Questions and answers are the lifeblood of learning, and we are all learning. I will answer all questions to the best of my ability and promise to keep personal information confidential.
Your genuine feedback and response are extremely valuable. Please suggest topics for the coming weeks.

Recent Comments