“Sustainable development is the development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs”: Gro Harlem Brundtland, Our Common Future (The Brundtland Report), 1987
Introduction
When we think about a family outing to a movie, there are 3 important ingredients. The first is a good movie, the second is the place where we are watching the movie and the last is snacks (popcorn). If all the 3 ingredients are in the right proportion, we can have a fulfilling evening.
Content: What are 3 Pillars of Sustainability
- What are the three pillars of sustainability (Economics, Environment and Society)?
- Why these three pillars are important?
- How they are interrelated with each other?
- Conclusion
Objective
To make an economic system sustainable, it is necessary to encourage energy generation from renewable sources, adopt policies and regulations that encourage energy efficiency, and the promotion of economic models based on the circular economy which, as such, can reduce waste and contain resource exploitation.
Once you go through the article, you will understand the meaning of the three pillars of sustainability (Economics, Environment and Society), why they are important, what is their purpose and how they are interrelated with each other.
Read More: https://bit.ly/LinearCircularEconomy
Definition: ISO 59004: 2024
Circular Economy (Cl 3.1.1): Economic system that uses a systematic approach to maintain a circular flow of resources by recovering, retaining or adding to their value while contributing to sustainable development.
Sustainable Development (Cl 3.1.11): Development that meets the environmental, social economic needs of the present without compromising the ability of the future generations to meet their own needs.
Life Cycle (Cl 3.2.4): Consecutive and interlinked stages in the life of a solution.
Linear Economy (Cl 3.5.10): Economic system where resources typically follow the pattern of extraction, production, use and disposal.
End of Life (Cl 3.5.30): <Product> point in time when a product is taken out of use and its resources are either recovered for processing or disposed of.
Life Cycle Assessment (Cl 3.6.8): Compilation and evaluation of the inputs, outputs and potential environmental impacts of a product system throughout its life cycle.
Read More: https://bit.ly/ReduceRecyleReuse
Detailed Information
As the world increasingly faces an urgent need to shift towards a more sustainable and regenerative economic model, the ISO 59000 family of standards emerges as a powerful catalyst for change. On 22 May 2024, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) published a new family of standards to guide the transition to the circular economy. The standards mark the first set of international definitions and rules for the circular economy.
Sustainability is an essential part of facing current and future global challenges, not only those related to the environment. It’s a holistic approach that considers the social, environmental and economic impacts of actions and decisions taken today.
Read More: https://bit.ly/ClimateChnages
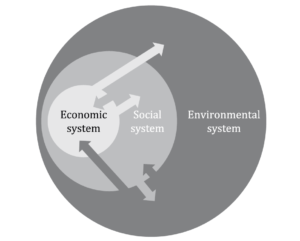 What is Environmental Sustainability?
What is Environmental Sustainability?
The environmental criterion analyses ecological impacts, such as CO2 emissions and the use of natural resources.
It is the ability to preserve and protect the natural environment over time through appropriate practices and policies, meeting present needs without compromising the availability of resources in the future.
Factors Influencing Environmental Sustainability:
- air, water and soil pollution.
- climate change is caused by the excessive amount of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere due to human activities.
- The loss of biodiversity.
- The overexploitation of natural resources.
- Economic models that involve unsustainable consumption.
What is Social Sustainability?
The social criterion considers aspects such as working conditions, human rights and the inclusion of people.
Social sustainability involves a focus on the well-being of people and communities. It’s about promoting equity, human rights, access to education and health care, and decent work while preserving social cohesion and justice.
Factors Influencing Social Sustainability:
- Poverty and socioeconomic inequality.
- Discrimination, prejudice and social exclusion.
- Lack of access to resources.
- Insecurity and conflict, locally, regionally and globally.
- Poor governance, which includes phenomena such as corruption and institutional inefficiency.
What is Economic Sustainability?
The Economic criteria evaluate transparency, business ethics and management.
It is the approach whereby economic activities are conducted in such a way as to preserve and promote long-term economic well-being. In practice, it aims to create a balance between economic growth, resource efficiency, social equity and financial stability.
Factors Influencing Economic Sustainability:
- The responsible management of resources.
- Financial stability at the macro level.
- International cooperation and partnerships between public administration and private enterprises.
- The level of equity and social inclusion.
- Corporate responsibility.
The linkage between 3 Pillars of Sustainability:
The pillars of sustainability are closely interconnected, in that every action taken within each of the spheres has spillover effects on the others.
- There is a strong interconnection between the environmental and economic spheres, where good environmental practices, such as responsible resource management, are essential to maintaining the stability of the economy and the very existence of the supply chain. Some sustainability strategies, such as transitioning to a low-carbon economy and adopting sustainable practices, can create economic opportunities, promote innovation and increase the competitiveness of businesses.
- The social sphere is also connected to the environmental and economic spheres. It is well established that in an equitable and inclusive society, where inequalities are reduced, social cohesion, active citizen participation and the basis for a sustainable and resilient economy are fostered – just as it is evident that people’s health and well-being are closely linked to the quality of the environment in which they live.
Conclusion:
- There are three pillars of sustainability: the environmental, the socially responsible, and the economic.
- Companies can improve their environmental sustainability by, for example, reducing their carbon footprint or wasteful practices.
- The social responsibility pillar represents practices that benefit the company’s employees, consumers, and the wider community.
- The economic (or governance) pillar refers to maintaining honest and transparent accounting practices and regulatory compliance.
Read More: https://bit.ly/ISO59000Series
References:
ISO 59004: 2024
ISO 59010: 2024
ISO 59020: 2024
Industry Experts
This is the 222nd article of this Quality Management series. Every weekend, you will find useful information that will make your Management System journey Productive. Please share it with your colleagues too.
In the words of Albert Einstein, “The important thing is never to stop questioning.” I invite you to ask anything about the above subject. Questions and answers are the lifeblood of learning, and we are all learning. I will answer all questions to the best of my ability and promise to keep personal information confidential.
Your genuine feedback and response are extremely valuable. Please suggest topics for the coming weeks.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.