Share our similarities and celebrate our differences: M. Scott Peck
Introduction
We interchangeably use the spelling of Principle and Principal assuming as same. Similarly, we often write there instead of their and vice versa. We sometimes use Stress for specifying the mechanical property and also for mental tension!
Objective
Verification and Validation go hand in hand and are often confused with each other although they have distinct meaning and purpose. While Verification is about objective evidence, Validation is primarily about subjective evidence. Both validation and verification are needed throughout the lifecycle.
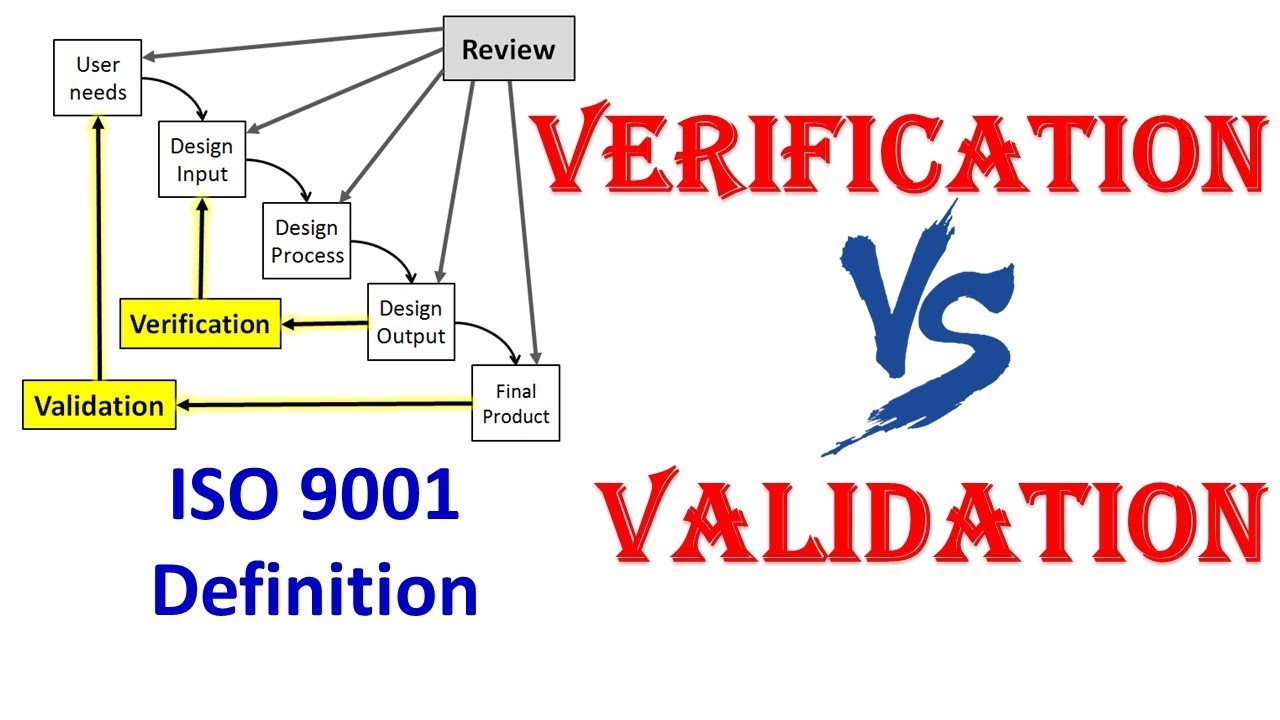
Definitions: ISO 9000: 2015
Verification (Cl 3.8.12): Confirmation through the provision of objective evidence that specified requirements have been fulfilled.
Validation (Cl 3.8.13): Confirmation through the provision of objective evidence that the requirements for the specific intended use or application have been fulfilled.
Detailed Information
As per ISO 9001: 2015 and IATF 16949: 2016, both Verification and Validation have their specific meaning and intent.
What is Verification?
It is a relatively objective process, in that if the various products and documents are expressed precisely enough, no subjective judgements should be needed.
What is Validation?
It is an extremely subjective process. It involves making subjective assessments of how well the (proposed) system addresses a real-world need. Validation includes activities such as requirements modelling, prototyping and user evaluation.
The key difference between Verification and Validation:
| S.No. | Verification | Validation |
| 1 | It is a Static Process | It is a Dynamic Process |
| 2 | Are we building the System right? | Are we building the right System? |
| 3 | “Building it right” checks that the specifications are correctly implemented by the system. | “Building the right thing” refers back to the user’s needs |
| 4 | Concerned with whether the system is well-engineered, error-free, and so on | Concerned with checking that the system will meet the customer’s actual needs |
| 5 | Verification will help to determine whether the product is of high quality | It will ensure that the system is useful to the user |
| 6 | Process of checking that the product meets the specification | Process of checking whether the specification captures the customer’s needs |
| 7 | Verification is done at many stages including Incoming Inspection, Record, Product configuration, Calibration, New Product Development, Change Control, Customer Property. Error Proofing, Job Setup | Validation is done at many stages including New Product Development, Product Testing, Control Plan, Supplier Development, Change Control, Embedded Software, Production Process-Revalidation |
| 8 | It is entirely possible that a product passes when verified as the product is built as per the specifications | It is entirely possible that a product fails when validated. This can happen when the specifications themselves fail to address the user’s needs |
Present Challenges:
- How often we read the definitions written in ISO 9000: 2015 & IATF 16949: 2016 and try to interpret it?
- During new product development process, how often we are clear about the desired output of Verification and Validation?
References:
IATF 16949: 2016
ISO 9002: 2015
ISO 9000: 2015
This is the 94th article of this Quality Management series. Every weekend, you will find useful information that will make your Management System journey Productive. Please share it with your colleagues too.
Your genuine feedback and response are extremely valuable. Please suggest topics for the coming weeks.
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.